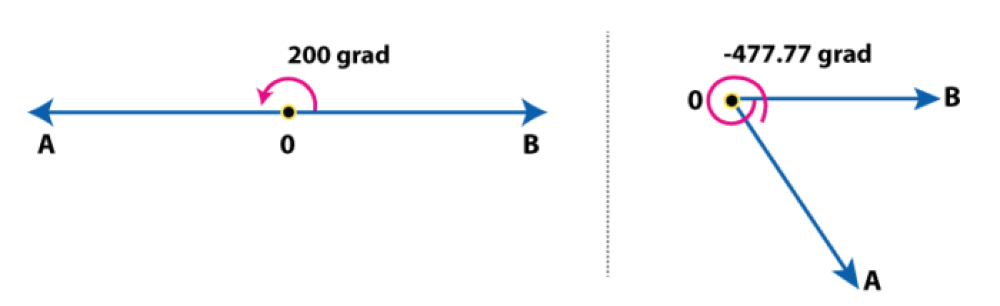
Angles: An Introduction

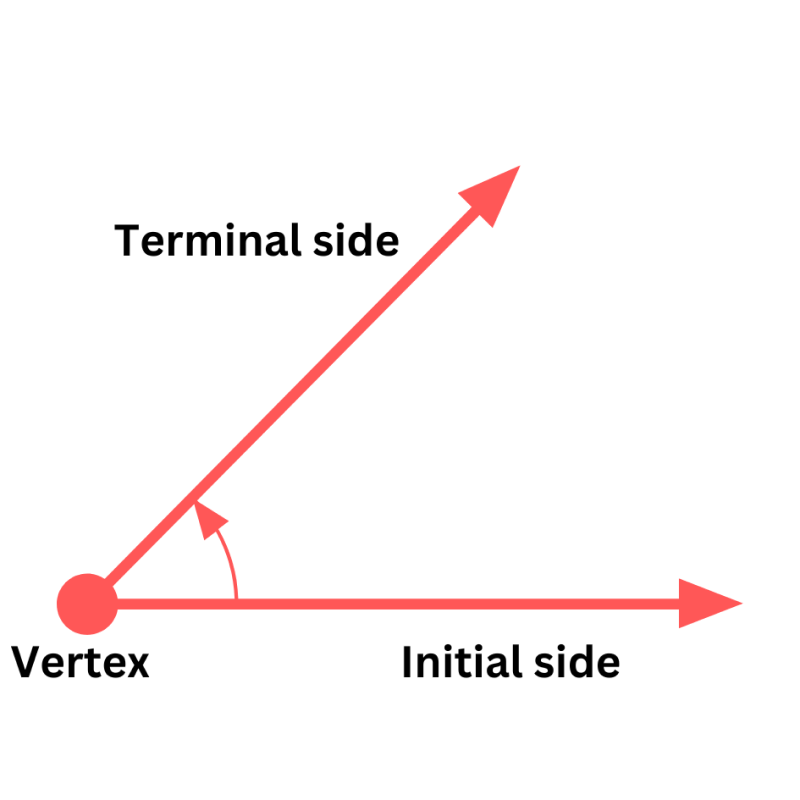
An angle is formed when two rays are joined together at a common point. The common point here is called node or vertex and the two rays are called arms of the angle. The angle is represented by the symbol ‘∠’. The word angle came from the Latin word “Angulus”. Learn more about lines and angles here. The angle is usually measured in degrees, using a protractor. Degrees 30°, 45°, 60°, 90°, 180° shows different angles here. The types of angles are based on the values of angles in degrees. We can also represent angles in radians, i.e., in terms of pi (π). 180 degrees is equal to π in radians.
Definition Of Angles
An angle is a form of geometrical shape, that is constructed by joining two rays to each other at their end-points. The angle can also be represented by three letters of the shape that define the angle, with the middle letter being where the angle actually is (i.e.its vertex). Angles are generally represented by Greek letters such as θ, α, β, etc.
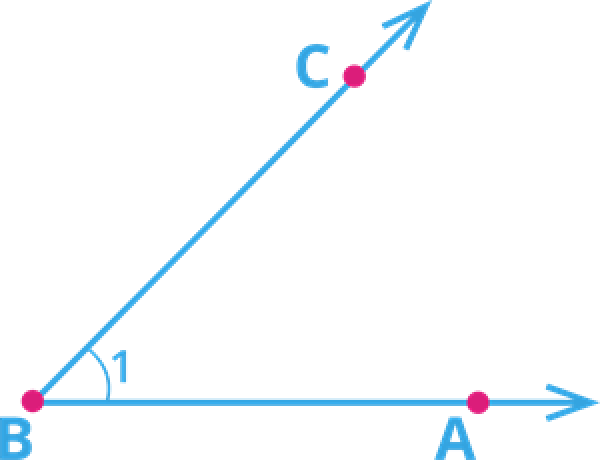
Eg. ∠ABC, where B is the given angle. Angle measurement terms are – degree °, radians or gradians. The amount of rotation about the point of intersection of two planes (or lines) which is required to bring one in correspondence with the other is called an Angle.
Types of Angles and Their Properties
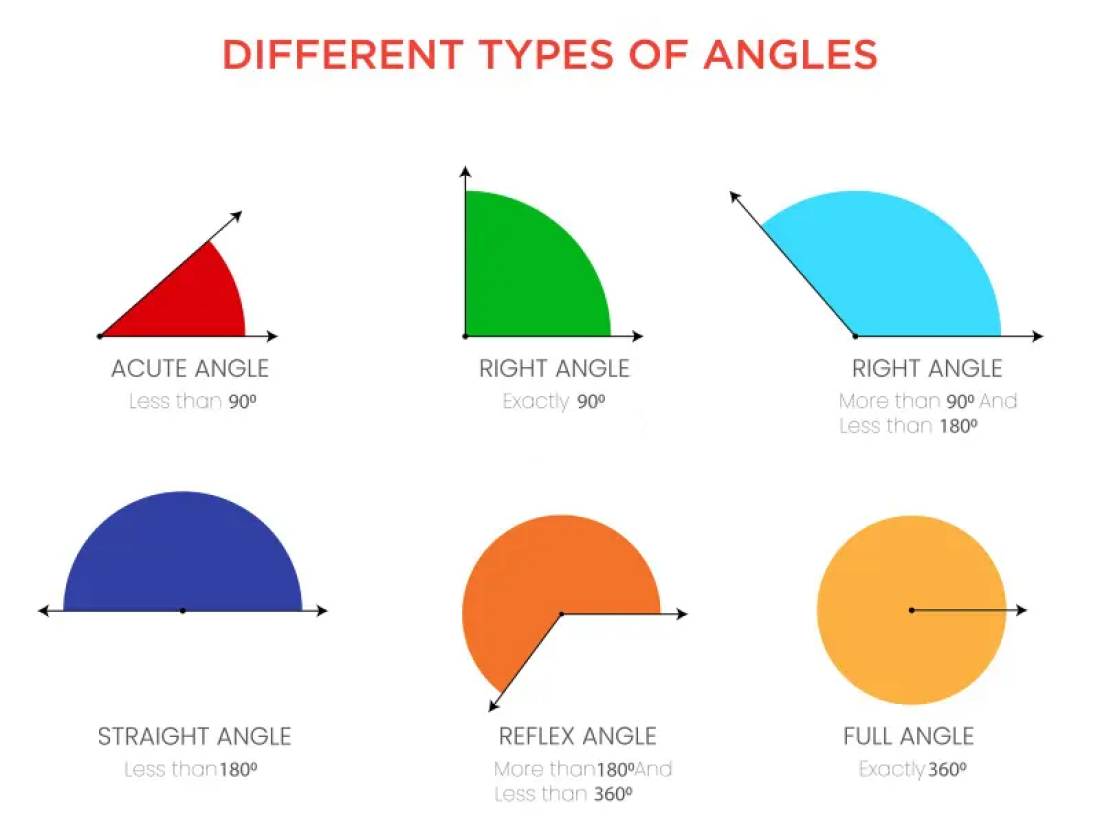
There are six types of angles. Each type of angle has a unique identification on the basis of angle measurement. Let us read about each type of angle individually along with their properties.
- Acute Angle: An acute angle is an angle which is greater than 0° and less than 90°.
- Right Angle: When an angle measures 90°, it is known as a right angle. A right angle can be easily observed as it forms the shape of the letter L.
- Obtuse Angle:When an angle measures greater than 90° but less than 180°, it is an obtuse angle.
- Straight Angle:Straight Angle: The angle formed by a straight line is called a straight angle. In other words, a straight angle is a straight line, and the angle formed between two rays is equal to 180°. At a straight angle, the two rays are opposite to each other. Two right angles make up a straight angle. Since the measure of a straight angle is 180°, it is one-half of the whole turn of a circle.
- Reflex Angle: A reflex angle is an angle whose measure is greater than 180° but less than 360°.
- Complete Angle: When the measurement of an angle is equal to 360° it is a complete angle.
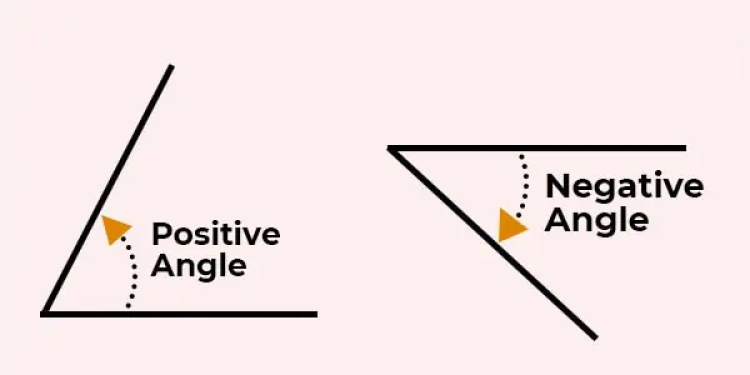
Angle Based on Rotation
Based on the direction of measurement or the direction of rotation, angles can be of two types: • Positive Angles • Negative Angles
Positive Angles:
An angle measured in the counterclockwise (anti-clockwise) direction is a positive angle. In other words, positive angles are those angles that are rotated from the base in the anti-clockwise direction.
Negative Angles:
Negative angles are those angles that are measured in a clockwise direction from the base. In other words, negative angles are those angles that are angles are rotated from the base in the clockwise direction.
 1.png)